Exhaust from diesel trucks and buses is a leading source of harmful air pollution that sends Massachusetts residents to the hospital every year.
Strong federal, state, and local policies are necessary to ensure a rapid and equitable transition to electric trucks and buses. A first step is adopting the Advanced Clean Truck (ACT) rule, a first-of-its kind regulation that requires manufacturers to sell an increasing percentage of electric trucks per year. Acknowledging the history of disproportionate air pollution impacts in Massachusetts, the ACT is only a first step of many that are necessary to guarantee pollution reductions in the communities that need it the most. Now is the time for Massachusetts to continue its climate and clean air leadership.
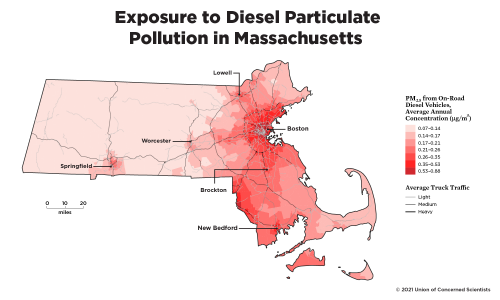
Exposure to Diesel Particulate Pollution in Massachusetts
Though medium and heavy-duty trucks and buses make up only 7 percent of the state’s 4.6 million registered vehicles , they contribute a disproportionate 46 percent of nitrogen oxide (NOx), 40 percent of fine particulate matter (PM2.5), and 20 percent of global warming emissions from all on-road vehicles.
Diesel exhaust contains a cocktail of toxic air pollutants that have led it to be deemed a Group 1 carcinogen by the World Health Organization. This includes NOx which irritates the heart and lungs and worsens the effects of asthma, especially in children and the elderly. NOx then further reacts in the atmosphere to form PM2.5 and ground-level ozone (soot and smog). PM2.5 is responsible for 63 percent of environmentally caused deaths in the US, and has been linked to premature death, increased hospital admissions for heart and lung diseases, bronchitis, and worsening of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
This pollution costs the state hundreds of millions of dollars and many lives lost. The map below shows how on-road diesel pollution from trucks and buses is concentrated in certain areas of the state, usually at the nexus of truck routes and other goods movement infrastructure (ports, warehouses, railyards, etc.). Diesel pollution exposure is especially high within the inner beltway (Route 128) surrounding Boston, given that it is one of the nation’s most densely populated cities and is the logistical center in the region. Other hotspots in the state follow the Mass Pike, I-93, and I-95, and occur in Gateway Cities such as Fall River, New Bedford, Brockton, Lawrence, Lowell, Springfield, Worcester, and areas east of Providence, Rhode Island. These hotspots overlap with the state’s communities that are already overburdened by the cumulative impacts of other environmental risks, social determinants of health, and socioeconomic vulnerabilities (see MassROUTES tool and the definition of environmental justice community in Massachusetts).
One promising route towards addressing toxic diesel pollution is the adoption of electric trucks and buses, which are available and ready today in most use cases and produce no tailpipe emissions. Transitioning to electric trucks and buses will not only allow Massachusetts residents to breathe more freely, but will also cut down on climate pollution, save money for truck and bus fleets, and result in lower electricity bills.
Strong federal, state, and local policies are necessary to ensure a rapid and equitable transition to electric trucks and buses. A first step is adopting the Advanced Clean Truck (ACT) rule, a first-of-its kind regulation that requires manufacturers to sell an increasing percentage of electric trucks per year. Acknowledging the history of disproportionate air pollution impacts in Massachusetts, the ACT is only a first step of many that are necessary to guarantee pollution reductions in the communities that need it the most. Now is the time for Massachusetts to continue its climate and clean air leadership.
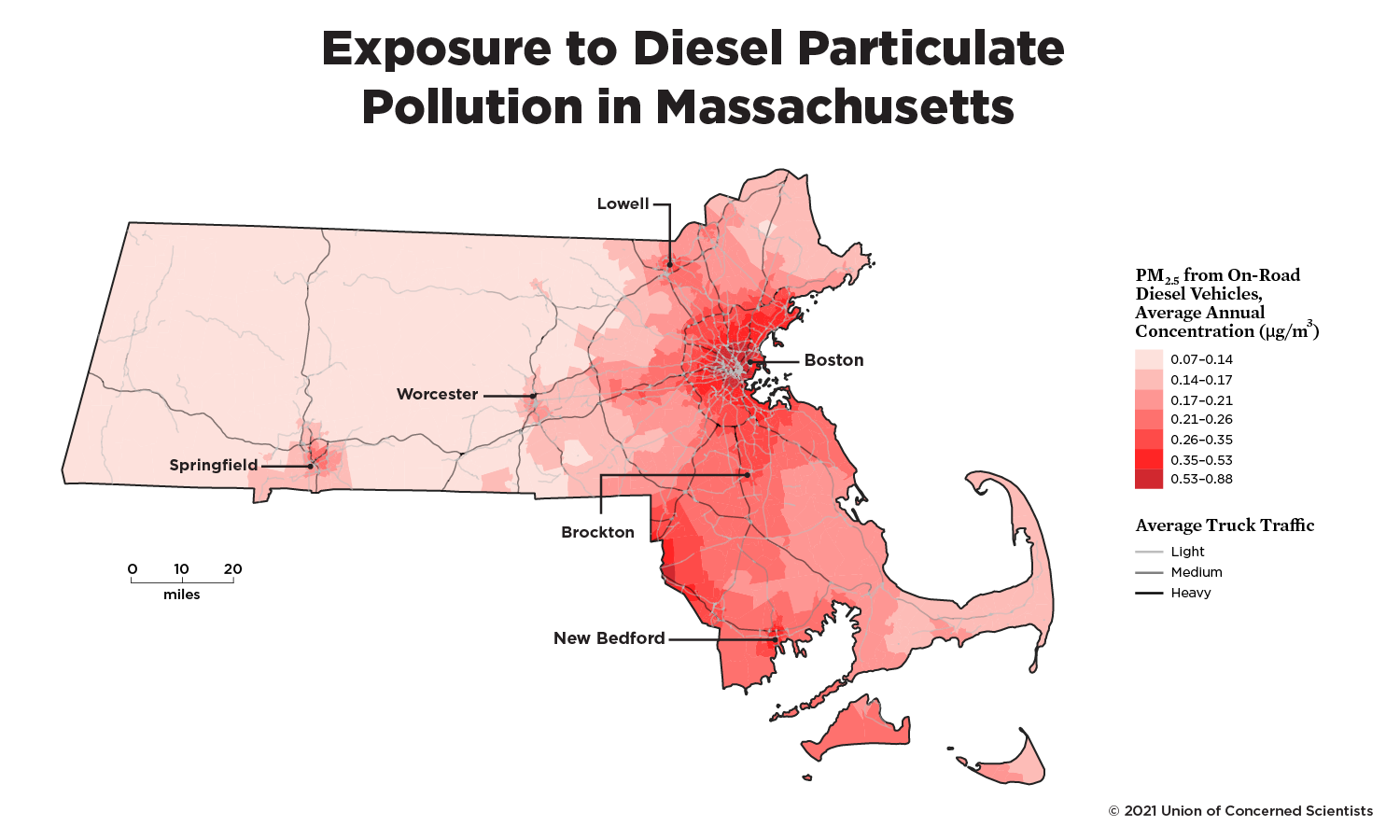
Note: this map shows pollution estimates based on a modeling tool and does not represent data from ground level air quality monitors. A deeper level of real-time data combined with the lived experiences of communities bearing the burden of this pollution is necessary to capture the full picture of this problem. EPA 2014; FHWA 2017; USCB 2019